File management
Naming
files:
It is important to keep the name of files short, this makes
it quick and easy to search and find images. When naming an image file you
should pick a meaningful name to do with the image for example an image of a
red door could be called “red_door” or “door_red”. This method makes it easy
for anyone to know what the file will contain. Another good way to name image
file is to stick to naming conventions such as using a _ instead of a space in
the file name.
 Using naming conversions and meaningful names improves the
organisation of files and make it considerably easier to find image files.
Using naming conversions and meaningful names improves the
organisation of files and make it considerably easier to find image files.
Folder
structures:
Folder
structures are an important part of maintaining organisations with files. Most
operating systems allow multiple folders to be created and then subfolder
within that folder, this allows for a complex but organised file layout. This
method of origination allows you to place image files into groups based on what
the images have in common. An example of this would be placing all the pictures
of laptops in one folder and in another folder all the pictures of Xbox 360.
Moving
files:
Moving files can be risky if certain precautions are not
taken to ensure that multiple copies of files are made, if these precautions
are not taken you run the risk of losing a file permanently.
Creating copies of an image file and moving to storage
device such as a USB stick is a good idea due to how easy it is to copy and
move files on the latest operating systems. One of the easiest and most common
ways of moving and copying files at the same time is to copy and paste the file
into the desired location.
Deleting
files:
Deleting files is an easy and basic operation on most
operating systems, but care should be taken when deleting files as hard drives
do have a data recovery system allowing files to be restored.
Vector and
Raster Graphics:
Raster (bitmap):
 Raster images are made of pixels of a set
colour and shades that create the image. Each raster image pixels represents a
different colour rather than an instruction, this is one of the main reasons
raster images are used in high detailed images or photographs. This file type
does not scale very well; this is because you are spreading the same image data
over a larger area. The image on the right is an example of how a raster reacts
to being scaled in comparison to a vector image.
Raster images are made of pixels of a set
colour and shades that create the image. Each raster image pixels represents a
different colour rather than an instruction, this is one of the main reasons
raster images are used in high detailed images or photographs. This file type
does not scale very well; this is because you are spreading the same image data
over a larger area. The image on the right is an example of how a raster reacts
to being scaled in comparison to a vector image.
GIF:
Graphics interchange format is a form of raster graphic. This
file format supports animation and transparency making it very popular on the internet;
this is also due to its quick loading times. GIF files support images up to 256
colours; this limitation causes GIF’s to have a poorer a quality in comparison to other
file formats.
Vector:
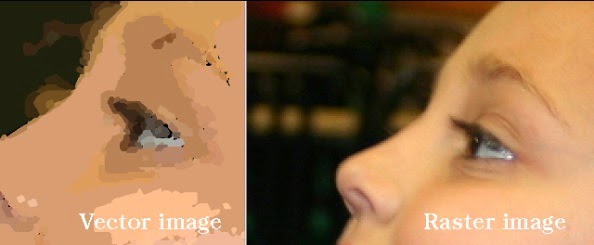 Vector images use a set of instruction to
create an image. This allows vector images to be scaled up and down without the
losing any of the image quality, this makes vector graphics the ideal file
format for a logo because it may need to be produced at multiple sizes. A major
disadvantage of this file format is its inability to handle complex graphics
such as a photo that could contain a large amount of different instructions. The
image on the right is an example of how a vector image cannot give the same graphical
quality of a photograph as a raster image.
Vector images use a set of instruction to
create an image. This allows vector images to be scaled up and down without the
losing any of the image quality, this makes vector graphics the ideal file
format for a logo because it may need to be produced at multiple sizes. A major
disadvantage of this file format is its inability to handle complex graphics
such as a photo that could contain a large amount of different instructions. The
image on the right is an example of how a vector image cannot give the same graphical
quality of a photograph as a raster image.
SVG:
Sizable vector graphics is a vector file format. This file
format is an all-purpose vector format. As with the majority of vector graphics
it cannot display photorealistic images very well .This file format supports animation
and transparency. It is commonly used on interactive web pages and is also
supported by the majority of modern browsers.
It is possible to reduce the file size of an image using
compression. The first method of compression is called lossy compression. Lossy
compression works by putting the colour information into blocks and eliminating
unnecessary bits of information, this in turn dramatically reduces the file
size. Once an image has been compressed you cannot get the original uncompressed
file back
The second method of file compression is lossless. This method allows the image to keep all of
its uncompressed data. It does this by using data algorithms; these algorithms
break the image data down for compression but also allow all of the data to be
fully restored.
good
ReplyDelete