Monday, 30 June 2014
Monday, 23 June 2014
Evolving Output Mediums (D1)
PDF:https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7Go5XyQzJkubjByYlNPTFU4bUk/edit?usp=sharing

 This
issue was solved with the introduction of the LCD monitor. The LCD monitor
allowed for a larger screen size and kept good colour depth. The LCD monitor is
still used in many products such as laptops.
This
issue was solved with the introduction of the LCD monitor. The LCD monitor
allowed for a larger screen size and kept good colour depth. The LCD monitor is
still used in many products such as laptops.
 Printers are a very important aspect of
digital graphics, because it allows digital graphics to be into a physical
graphic. Printers have been improving in the amount of dots per inch (DPI) ever
since the first inkjet was released in 1998. A high DPI is vital for the best
quality images, without a high DPI the images that a printer produces are of a
poor quality.
Printers are a very important aspect of
digital graphics, because it allows digital graphics to be into a physical
graphic. Printers have been improving in the amount of dots per inch (DPI) ever
since the first inkjet was released in 1998. A high DPI is vital for the best
quality images, without a high DPI the images that a printer produces are of a
poor quality.
 Companies
such adobe are now capitalising on how effective mobile phone are as an output
medium, by realising apps such as “Photoshop express”, applications such as
this provide mobile users with some of the features they would get from the PC
versions of these products
Companies
such adobe are now capitalising on how effective mobile phone are as an output
medium, by realising apps such as “Photoshop express”, applications such as
this provide mobile users with some of the features they would get from the PC
versions of these products
Evolving Output Mediums:

Monitors:
In the late 1980s CRT monitors were commonly used in the
creation of graphical images. CRT monitors provided good colour depth for the
creation of graphical images. A major disadvantage to the CRT monitor was the
fact that they came in small sizes. This was an issue because bigger screen
sizes allow for higher resolution image creation.
 This
issue was solved with the introduction of the LCD monitor. The LCD monitor
allowed for a larger screen size and kept good colour depth. The LCD monitor is
still used in many products such as laptops.
This
issue was solved with the introduction of the LCD monitor. The LCD monitor
allowed for a larger screen size and kept good colour depth. The LCD monitor is
still used in many products such as laptops.
LCD monitors have been improved with IPS technology. This
technology is useful in term of graphical design, because it allows for a strong
viewing angle and it displays deeper colours correctly. This technology has
improved the efficiency of graphical design
Printers:
 Printers are a very important aspect of
digital graphics, because it allows digital graphics to be into a physical
graphic. Printers have been improving in the amount of dots per inch (DPI) ever
since the first inkjet was released in 1998. A high DPI is vital for the best
quality images, without a high DPI the images that a printer produces are of a
poor quality.
Printers are a very important aspect of
digital graphics, because it allows digital graphics to be into a physical
graphic. Printers have been improving in the amount of dots per inch (DPI) ever
since the first inkjet was released in 1998. A high DPI is vital for the best
quality images, without a high DPI the images that a printer produces are of a
poor quality.
Printers have also been evolving in term
of their connectivity. Printers now come with Wi-Fi capabilities, this allows
for wireless printing. Wireless printing is now an important part of most work
places, and makes printing for employees a lot easier and less time consuming.
Printers have also started to included other technology such
as scanners, this is particularly useful in terms of digital graphics because
it allows a physical graphic to be converted to a digital graphic that can then
be manipulated.
Mobile phones are an example of an output
medium for digital graphics that is rapidly evolving. Mobile phones have
evolved from being limited to only making phone calls, to now being able to
take 1080p videos and edit them. This is a quite a drastic leap considering how
quickly this evolution happened.
 Companies
such adobe are now capitalising on how effective mobile phone are as an output
medium, by realising apps such as “Photoshop express”, applications such as
this provide mobile users with some of the features they would get from the PC
versions of these products
Companies
such adobe are now capitalising on how effective mobile phone are as an output
medium, by realising apps such as “Photoshop express”, applications such as
this provide mobile users with some of the features they would get from the PC
versions of these products
Tuesday, 17 June 2014
Justification of software and hardware (M2)
PDF:https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7Go5XyQzJkuR29hLUY2QlcwQjQ/edit?usp=sharing
Justification for Graphical Image:
Software:
The software I used to create and manipulate my graphical image was Photoshop. I chose Photoshop because I am fairly familiar with its UI, and I fell that it has a greater number of tutorials if needed them. This software worked very well for me due to its use of a layering system that allowed me to manipulate different images easily and effectively.
Hardware:
Mouse and Keyboard
I chose to use these two tools because the UI for Photoshop is easy to navigate with the use of a mouse. Photoshop also includes a lot of keyboard shortcuts that allowed me to access tools and function such as transform, quickly and efficiently.
I didn't find any use for a graphics tablet due to the fact was not creating my own images from scratch
Resolution:
I chose to make my image 500x500. I picked this resolution to make a completely square graphical image. I also felt that this resolution would be sufficiently large enough so that the image would not have to be scaled up for viewing.
Colour depth:
I chose to use 24bit colour in my image because it generally considered a standard size. 24bit colour has provided my image with vibrant colours, that can be seen well even when scaled.
File format:
I chose to save my image in a JPEG format, because it is very good at producing a good quality image with a relatively small file size Limitations of Different Hardware and Software: (M1)
PDF:https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7Go5XyQzJkuaXl1eHloeWMxR2M/edit?usp=sharing
Hardware:
Name:
|
Limitations:
|
Mouse
|
In terms of graphic design the mouse isn’t a great
piece of hardware in terms of making an image. This is because it is hard to
control and doesn’t feel natural to draw an image with.
In comparison with a graphics tablet the mouse is
very basic. With a mouse you have to select a specific opacity before drawing
line, a graphics tablet allows you to decide this by registering pressure
applied when drawing.
Drawing straight or curved lines is extremely
difficult and that in turn forces you to use the tools provided in software.
|
Graphics tablet
|
The graphics tablet is specifically designed for
graphic design and provides the user with much more freedom than the mouse in
term of drawing.
Although when it comes to navigating menus it becomes
much less effective than the mouse.
It also becomes a lot less usable in terms of using
specific tools such as rotation and moving images.
|
Software:
Name:
|
Limitations
|
Photoshop
|
Photoshop is not as user friendly as other software such as gimp, this is due to its UI which is relatively difficult to modify in comparison to GIMP
Photoshop is limited to newer systems due to the 1GB of RAM required to run. Photoshop is also now available on some operating systems such as Linux
Photoshop also has a small variety of free effects in comparison to other software such as GIMP
|
Gimp
|
GIMP is limited to only being able to manipulate 8 bit images. This is a huge disadvantage because Photoshop is able to work with 8,16 and 32 bit images
The files that GIMP creates (XCF) cannot be opened in Photoshop, but Photoshop files can be opened in GIMP. This is a limitation to users who want to use both piece of software on a single project
|
Tuesday, 1 April 2014
Marquee Development (P4,P5)
Marquee
Development Log
This is a development log for the marquee that was made to
go on the arcade cabinet, it is used to attract people to play my game Hunter
Using the feedback I had previously received a I changed the background of my marquee to make it stand out more.
When I then resubmitted my marquee to get more peer reviews
on my new version, I then used the constructive feedback received to create a
new and improved version.
I used the feedback from my peers to create my final
marquee. It was suggested that I try to make the helmet look as if it is
embedded it the marquee. It was also suggested that I add out glows to my text
and logo to make the marquee stand out more.
Poster Development (P4,P5)
Hunter
Poster Development Log:
This was the first version of my poster that I created.
Once I had finished my poster shared it with my peers over
social media sites asking for feedback, the feedback received was very
constructive and the overall message I received from it was that I need to
include the title of my game.
I then resubmitted my poster for my peers to review again. The second set of feedback I received told me to change the font to a darker red and add some effects.
File Formats (P2)
File management
Naming
files:
It is important to keep the name of files short, this makes
it quick and easy to search and find images. When naming an image file you
should pick a meaningful name to do with the image for example an image of a
red door could be called “red_door” or “door_red”. This method makes it easy
for anyone to know what the file will contain. Another good way to name image
file is to stick to naming conventions such as using a _ instead of a space in
the file name.
 Using naming conversions and meaningful names improves the
organisation of files and make it considerably easier to find image files.
Using naming conversions and meaningful names improves the
organisation of files and make it considerably easier to find image files.
Folder
structures:
Folder
structures are an important part of maintaining organisations with files. Most
operating systems allow multiple folders to be created and then subfolder
within that folder, this allows for a complex but organised file layout. This
method of origination allows you to place image files into groups based on what
the images have in common. An example of this would be placing all the pictures
of laptops in one folder and in another folder all the pictures of Xbox 360.
Moving
files:
Moving files can be risky if certain precautions are not
taken to ensure that multiple copies of files are made, if these precautions
are not taken you run the risk of losing a file permanently.
Creating copies of an image file and moving to storage
device such as a USB stick is a good idea due to how easy it is to copy and
move files on the latest operating systems. One of the easiest and most common
ways of moving and copying files at the same time is to copy and paste the file
into the desired location.
Deleting
files:
Deleting files is an easy and basic operation on most
operating systems, but care should be taken when deleting files as hard drives
do have a data recovery system allowing files to be restored.
Vector and
Raster Graphics:
Raster (bitmap):
 Raster images are made of pixels of a set
colour and shades that create the image. Each raster image pixels represents a
different colour rather than an instruction, this is one of the main reasons
raster images are used in high detailed images or photographs. This file type
does not scale very well; this is because you are spreading the same image data
over a larger area. The image on the right is an example of how a raster reacts
to being scaled in comparison to a vector image.
Raster images are made of pixels of a set
colour and shades that create the image. Each raster image pixels represents a
different colour rather than an instruction, this is one of the main reasons
raster images are used in high detailed images or photographs. This file type
does not scale very well; this is because you are spreading the same image data
over a larger area. The image on the right is an example of how a raster reacts
to being scaled in comparison to a vector image.
GIF:
Graphics interchange format is a form of raster graphic. This
file format supports animation and transparency making it very popular on the internet;
this is also due to its quick loading times. GIF files support images up to 256
colours; this limitation causes GIF’s to have a poorer a quality in comparison to other
file formats.
Vector:
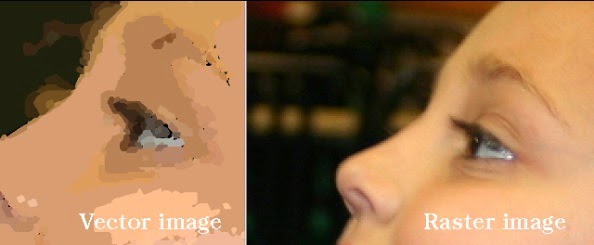 Vector images use a set of instruction to
create an image. This allows vector images to be scaled up and down without the
losing any of the image quality, this makes vector graphics the ideal file
format for a logo because it may need to be produced at multiple sizes. A major
disadvantage of this file format is its inability to handle complex graphics
such as a photo that could contain a large amount of different instructions. The
image on the right is an example of how a vector image cannot give the same graphical
quality of a photograph as a raster image.
Vector images use a set of instruction to
create an image. This allows vector images to be scaled up and down without the
losing any of the image quality, this makes vector graphics the ideal file
format for a logo because it may need to be produced at multiple sizes. A major
disadvantage of this file format is its inability to handle complex graphics
such as a photo that could contain a large amount of different instructions. The
image on the right is an example of how a vector image cannot give the same graphical
quality of a photograph as a raster image.
SVG:
Sizable vector graphics is a vector file format. This file
format is an all-purpose vector format. As with the majority of vector graphics
it cannot display photorealistic images very well .This file format supports animation
and transparency. It is commonly used on interactive web pages and is also
supported by the majority of modern browsers.
It is possible to reduce the file size of an image using
compression. The first method of compression is called lossy compression. Lossy
compression works by putting the colour information into blocks and eliminating
unnecessary bits of information, this in turn dramatically reduces the file
size. Once an image has been compressed you cannot get the original uncompressed
file back
The second method of file compression is lossless. This method allows the image to keep all of
its uncompressed data. It does this by using data algorithms; these algorithms
break the image data down for compression but also allow all of the data to be
fully restored.
Monday, 31 March 2014
Hardware and Software Required to Work with Graphic Images (P1)
PDFhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7Go5XyQzJkuYlhPdWNGWEJiYjQ/edit?usp=sharing
Hardware and Software used in Digital Graphics
Hardware:
Name:
|
Description:
|
Purpose:
|
Monitor
|
A form of output device, comes in a wide verity of forms such as: LCD, LED and CRT
|
Displays images so the user can visually edit the image
|
Mouse
|
A form of input device, normally connected to a device via USB
|
Allows the user to edit an image using movement. Works in conjunction with the monitor to visually edit images
|
Keyboard
|
A form of input device
Normally connected to a device via USB
|
Allows the user to use graphic editing software more efficiently by using shortcuts
It also allows the input of text
|
Graphics Card
|
A form of output device.
This device allows for powerful and efficient rendering
|
Specifically designed to render graphics, also allows for advanced effects and filters
|
Central processing unit
|
A form of output device
This device will render graphics if a Graphics card is not available
|
Similar to a graphics card although not as efficient because it’s not specifically designed for this purpose
|
RAM
|
A form of volatile storage
|
Allows the user to access large amounts of image data quickly
|
USB
|
A form of non-volatile memory
Portable flash storage memory
Ranges from 128mb to 256gb
|
Allows the user to create backups and easily move files to different systems
|
Hard disk drive
|
A form of non-volatile memory used for storing a large amount of files
|
Allows the user to save finished work and work in progress, also allows them to store all the graphic editing software needed
|
Printer
|
A form of output device, normally connected via USB
A large amount of types available such as: Ink jet, laser and plotter
|
Allows the user to make digital images into physical images via the use of a material such as paper
|
Scanner
|
A form of input device
Normally connected via USB
|
Allows for the transformation of a physical image to a digital image that can then be digitally edited
|
Software:
Software:
|
Description:
|
Purpose:
|
Operating systems
|
Allows a user to interact with a computer
Also manages the computers resources
|
The OS allows the user to run graphic editing software such as Photoshop
|
Graphical editing software
|
A piece of software specifically designed to edit images
|
Graphical editing software allows a user to edit and manipulate an image
|
Internet browser
|
Allows the user access to the world wide web
|
An internet browser can be used to find recourses such as royalty free images.
It can also be used to download new graphical editing software
|
Image viewer
|
A piece of software that allows the display of digital graphics in a verity of file types
|
This software allows a user to view different images, although the editing that can be done is extremely limited
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)








